Intent-based Networking (IBN) is a known paradigm in network management that applies AI and network orchestration to automate tasks within the network without revealing the details of specific solutions used. “Intent”, which is the basis of IBN refers to a performance or policy objective in managing the IT infrastructure. Most of IBN systems are characterised by most or all of the five major functionalities which include: intent profiling, translation, resolution, activation and assurance (Leivadeas et al, 2023).
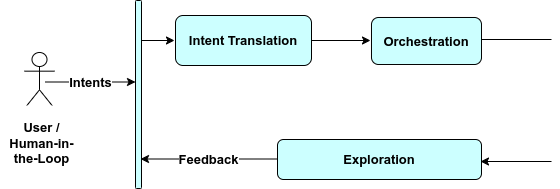
Three of the core elements of IBN based on the functionalities outlined above that are proposed to be adopted in the CyclOps project are: (i) the translation of user intents to low-level machine-understandable structure through Natural Language Processing; (ii) the orchestration of resources to fulfill data life-cycle process management as desired by the user, which belongs to intent activation; and (iii) the human-in-the-loop which belongs to the intent assurance functionality. The use of IBN is also laced with several challenges including: intent profiling, intent translation difficulties, unfavourable conditions of the IT infrastructure, etc.
Nevertheless, from the CyclOps perspective, intent-based system would be of immense benefits which include: reducing the complexity of creating, managing and enforcing data lifecycle policies; minimising the human effort and errors associated with retrieving and/or processing and manipulating specific data according to users’ desires; bridging the gap between non-technical users and the CyclOps automated systems, among others.
The CyclOps architecture contains a dedicated module called Intent-based Human Interface, which is tasked with retrieving and processing user requirements. CyclOps then deploys data lifecycle pipelines automatically with the aim of fulfilling these requirements.
The user enters an intent and CyclOps deploys the pipeline to enforce that intent and also allows for human interpretation of the results. This showcases a combination of automation and human involvement in the CyclOps ecosystem, realised by applying human-in-the-loop – an element of IBN as highlighted above.
In the CyclOps project, human-in-the-loop approaches are highly valued for ensuring the quality and reliability of data at many stages. With the help of the Exploratory Analysis Engine, a component of the Intent-based Human Interface, users are able to select their preferred range of data or data services. Users can also interpret the results and make decisions based on them.
For instance, CyclOps modules utilising AI might highlight trends or correlations during data analysis based on the user’s defined intent. However, the user would be expected to interpret these findings to make informed business decisions.
By integrating human expertise with technical capabilities, IBN will optimize CyclOps data life cycle management processes, resulting in more robust and reliable outcomes.
Reference
- Leivadeas and M. Falkner, “A Survey on Intent-Based Networking,” in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 625-655, Firstquarter 2023, doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3215919.

